- +49 (0)159 0653 1595
- CONTACT US

HOMEMachining services

Tungsten is known for its exceptional heat resistance and excellent radiation shielding properties. However, due to its high hardness and tendency to crack or chip during machining, it is classified as a “difficult-to-machine material.”
| Chemical Formula | Melting Point | Thermal Conductivity | Thermal Expansion Coefficient | Density | Mohs Hardness |
| W | 3,422℃ | 168W/m・K | 4.3(10−6/K) | 19.3g/㎤ | 9 |
| Material Characteristics ・High melting point allows for use in ultra-high-temperature environments. ・Low thermal expansion coefficient ensures excellent shape stability under extreme heat, minimizing distortion or warping. ・High metal density provides superior radiation shielding properties. |
|||||

Molybdenum has machinability comparable to stainless steel, making it relatively easier to process among refractory metals. While it shares similar properties with tungsten, it has lower heat resistance. As a result, it is used selectively depending on the specific application and environmental requirements.
| Chemical Formula | Melting Point | Thermal Conductivity | Thermal Expansion Coefficient | Density | Mohs Hardness |
| Mo | 2,623℃ | 142W/m・K | 5.1(10−6/K) | 10.28g/㎤ | 5.5 |
| Material Characteristics ・High melting point allows for use in ultra-high-temperature environments. ・Low thermal expansion coefficient ensures excellent shape stability under extreme heat, minimizing distortion or warping. ・Superior machinability allows for the processing of complex shapes. |
|||||

Unlike sintered metals such as tungsten and molybdenum, tantalum is manufactured through a melting process, resulting in fewer material defects and making it a high-performance material. However, due to its ductility, it is considered a challenging material for cutting and machining processes.
| Chemical Formula | Melting Point | Thermal Conductivity | Thermal Expansion Coefficient | Density | Mohs Hardness |
| Ta | 3,269℃ | 57.5W/m・K | 6.4(10−6/K) | 16.65g/㎤ | 6.5 |
| Material Characteristics ・High melting point allows for use in ultra-high-temperature environments. ・Offers flexibility and ductility not found in tungsten or molybdenum. ・High dielectric constant allows it to be widely used in capacitor applications. |
|||||

Material: Tungsten, Molybdenum, etc.
Even for hard-to-machine materials, we handle requests requiring high precision, such as curved surface machining for outer edges or slits.
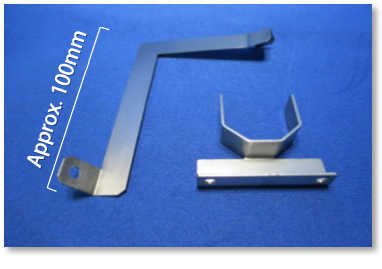
Material: Molybdenum
We handle sheet metal processing of molybdenum, which, being a sintered metal, lacks flexibility and is prone to cracking.
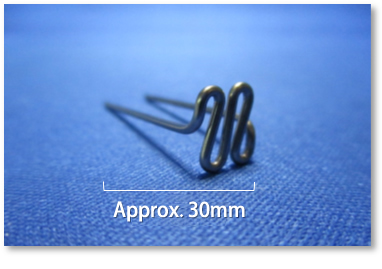
Material: Tungsten
Even with hard materials like tungsten, we can perform precise bending into complex shapes. We also handle requests requiring uniform gap formation with high accuracy.
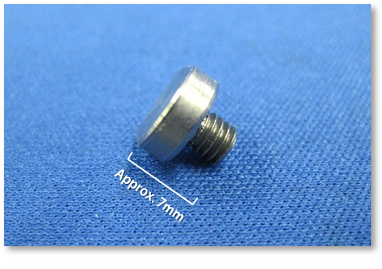
Material: Tantalum
Despite its high ductility and machining difficulty, we can produce precise components using tantalum.